|
|
Definition |
Illustration |
|
|
|
|
|
1 |
||
|
2 |
||
|
3 |
||
|
4 |
||
|
5 |
||
|
6 |
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
7 |
Figure 2 |
|
|
8 |
Figure 7 |
|
|
9 |
Figure 8 |
|
|
10 |
Figure 9 |
|
|
11 |
||
|
12 |
||
|
13 |
||
|
14 |
Figure 20 |
|
|
15 |
||
|
16 |
Figure 25 |
|
|
17 |
||
|
18 |
||
|
19 |
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
20 |
eAea |
|
|
21 |
Figure 3 |
|
|
22 |
||
|
23 |
||
|
24 |
||
|
25 |
Figure 21 |
|
|
26 |
||
|
27 |
||
|
28 |
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
Undefined Terms |
|
|
|
conduction |
Figure 6 |
|
|
deformation |
Figure 11 |
|
|
epicenter |
Figure 13 |
|
|
focus |
Figure 15 |
|
|
hot spot |
Figure 18 |
|
|
magnitude |
Figure 22 |
|
|
meteorologist |
Figure 24 |
|
|
oceanic crust |
Figure 27 |
|
|
oceanographer |
Figure 28 |
|
|
plate |
Figure 31 |
|
|
radiation |
Figure 33 |
|
|
rift valley |
Figure 35 |
|
|
seismograph |
Figure 38 |
|
|
SONAR |
Figure 40 |
|
|
subduction |
Figure 42 |
|
|
tsunami |
Figure 44 |
- Earthquake
An
earthquake is a sudden movement of the earthfs surface.
Figure 12:
Earthquake (epicenters)
- Fault
A fault breaks the earthfs surface when rocks slip past each other .
Figure 14: Fault (San Andreas)

·
Normal Fault
A normal fault is when a block of rock lies above the fault and another
block of rock lies below the fault.
·
Reverse Fault
A reverse fault is when a hanging wall slides up past the foot wall.
·
Seismic Waves
A traveling vibration
released by earthquakes.
Figure 37:
Seismic Waves, Body & Surface

·
Strike-Slip Fault
A strike slip
fault is when rocks on either side of the fault slide past each other sideways,
with little up or down motion.
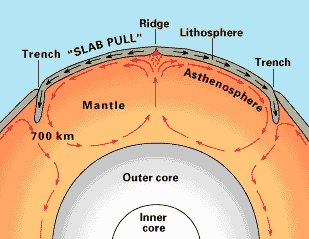
· Asthenosphere
Asthenosphere is the
layer of the earth below the lithosphere.
The continental crust
is the first layer of the earth(from the top) and is the layer that we walk on.
·
Continental Drift
The hypothesis of Alfred Wegener that the continents moved across the
earthfs surface.
·
Convection
Heat transferred by
the movement of heated fluid.
·
Core
This layer is a dense ball of solid metal and it's found inside of the outer
core and is the last layer of the earth(center).

·
Fossil
A trace of an
organism that has been preserved in a rock for millions of years.
A geologist is a
scientist that studies rock, fossils, and solids.
Figure 17: Alfred Wegener

Lithosphere is the most upper part of the mantle.
The mantle is the layer below the crust of the earthfs
surface and is made of hard rock; it is divided into 2 different layers, upper
mantle and lower mantle.
Molten
materials rises from the mantle then spreads out, pushing and spreading the
older rock to either side of the ridge under the ocean.
The name of single land mass that has broken apart over 2
hundred million years ago.
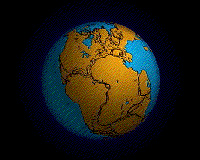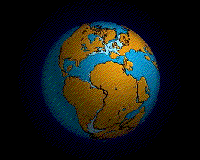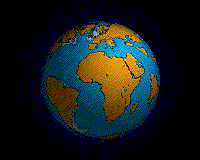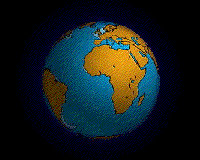
Pieces of earthfs lithosphere are in constant motion
driven by convection currents in the mantle.

A trench is when the
oceanic crust goes underneath the continental crust and subduction occurs.
·
eAea
Slow moving lava that is cooler than
pahoehoe.

·
Batholith
A large mass of rock when lava cools inside earthfs crust.
A cinder cone is a steep coned shaped hill or mountain
made up volcanic ash and bombs piled up around a volcano opening.
Figure 4: Example of Cinder Cone (Mt.
Fuji)

A tall cone shaped
mountain in which layers of lava alternate with layers of ash and volcanic
materials.
Figure 5:
Composite Volcano (Mount Ranier)

Lava is when magma comes and reaches the earth's surface
through a volcanic vent.

Magma is the pocket beneath the volcano where magna collects.
Pahoehoe is
fast moving lava and is hotter than eafa.

A major belt
of volcanoes that rims the Pacific Ocean.
A wide gentle sloping
mountain made of layers of lava and itfs from quiet eruptions.
Figure 39:
Shield Volcano (Mauna Kea)